Motional EMF
Motional EMF: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Motional Emf in a Conductor, Fleming's Right Hand Rule for Induced Current, Derivation of Motional Emf, Motional Emf in Curved Conducting Wire, Motional Emf in a Rotating Conducting Rod, etc.
Important Questions on Motional EMF
A jet plane is travelling towards wets at a speed of . What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of , if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of and the dip angle is ?
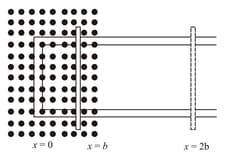
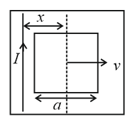
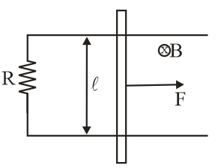
Figure shows a rectangular conductor in which the conductor is free to move in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The field extends from to and is zero for . Assume that only the arm possesses resistance . When the arm is pulled outward from with constant speed , the joules heating loss from would be:
The figure given below shows an arrangement by which current flows through the bulb (X) connected with coil B, when a.c. is passed through coil A.
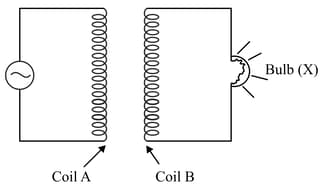
(i) Name the phenomenon involved.
(ii) If a copper sheet is inserted in the gap between the coils, explain how the brightness of the bulb would change.
A loop is moving with velocity towards the right. The magnetic field is . Loop is connected to a resistance of . If the steady current of flows in the loop, then the value of , if loop has resistance of , is (Given )
The figure shows a rod of length with points and on it. The rod is moved in a uniform magnetic field in different ways as shown. In which case, the potential difference between and is minimum?
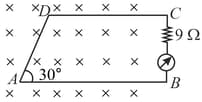
A conducting square frame of side and a long straight wire carrying current are located in the same plane as shown in the figure. The frame moves to the right with a constant velocity . The emf induced in the frame will be proportional to:
A thin semicircular conducting ring () of radius is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field , as shown in the figure. The potential difference developed across the ring whẹn its speed is , is:
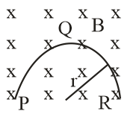
A metallic rod of length is tied to a string of length and made to rotate with angular speed on a horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If there is a vertical magnetic field in the region, the e.m.f. induced across the ends of the rod is:
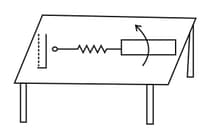
Assertion: Consider the arrangement shown below. A smooth conducting rod, , is lying on a smooth shaped conducting wire making good electrical contact with it. The shape conducting wire is fixed and lies in a horizontal plane. There is a uniform and constant magnetic field in the vertical direction (perpendicular to the plane of the page in the figure). If the magnetic field strength is decreased, the rod moves towards the right.
Reason: In the situation of statement, the direction in which the rod will slide is that which tends to maintain constant flux through the loop. Providing a larger loop area counteracts the decrease in magnetic flux. So the rod moves to the right independent of the fact that the direction of the magnetic field is into the page or out of the page.
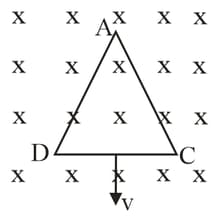
An equilateral triangular loop having some resistance is pulled with a constant velocity out of a uniform magnetic field directed into the paper. At time , side of the loop is at the edge of the magnetic field. The induced current versus time graph will be as
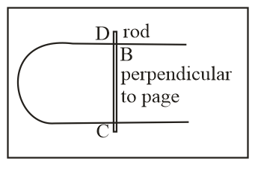
A conducting ring is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. An emf is induced in the ring if
For given arrangement (in horizontal plane) the possible direction of magnetic field:
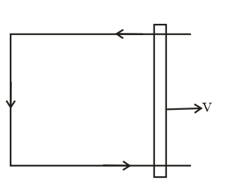
A constant force is being applied on a rod of length kept at rest on two parallel conducting rails connected at ends by resistance in uniform magnetic field as shown.
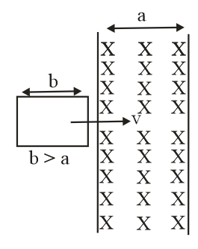
In the given arrangement, the loop is moved with constant velocity in a uniform magnetic field in a restricted region of width . The time for which the emf is induced in the circuit is:
A conducting ring lies fixed on a horizontal plane. If a charged nonmagnetic particle is released from a point (on the axis) at some height from the plane, then:
A semicircular wire of radius is rotated with constant angular velocity about an axis passing through one end and perpendicular to the plane of the wire. There is a uniform magnetic field of strength . The induced e.m.f. between the ends is:
A rectangular coil has turns and its length and width is and respectively. The coil rotates at a speed of rotation per minute in a uniform magnetic field of . Then the maximum induced emf will be-
An athelete runs at a velocity of , towards east with a rod. The horizontal component of the earth is . If he runs, keeping the rod (i) horizontal and (ii) vertical, the p.d. at the ends of the rod in both the cases, will be-
A straight conductor of length is moved in a magnetic field of with a velocity of . The maximum emf induced in the conductor will be -
An aeroplane having a distance of between the edges of its wings is flying horizontally with a speed of . If the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field is , then the induced emf will be -
